Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum have taken the world by storm. While many are intrigued by the potential profits of crypto mining, cybercriminals have found a way to exploit this trend through what’s known as “crypto mining malware.”
Crypto mining malware is a type of malicious software designed to hijack the computational power of an unsuspecting user’s device. Instead of the traditional mining process, where individuals use their own resources to validate and record cryptocurrency transactions, this malware operates covertly. It silently uses a victim’s device to mine cryptocurrencies, benefiting the attacker while leaving the user with slowed device performance, increased electricity bills, and potential hardware damage.
The implications of such malware are vast. Beyond the immediate effects on device performance, there’s a broader concern about privacy and security. These malicious programs can often be bundled with other types of malware, leading to data breaches, the loss of sensitive information, or even financial losses.
Given these risks, it’s of paramount importance to remove crypto mining malware from affected devices. Not only does this protect the individual user, but it also contributes to a safer digital ecosystem, preventing cybercriminals from profiting off unsuspecting victims.
As we explore this topic, we’ll equip you with the knowledge and tools to detect, combat, and prevent these stealthy threats, ensuring your digital safety in the cryptocurrency era.
How Does Crypto Mining Malware Work?
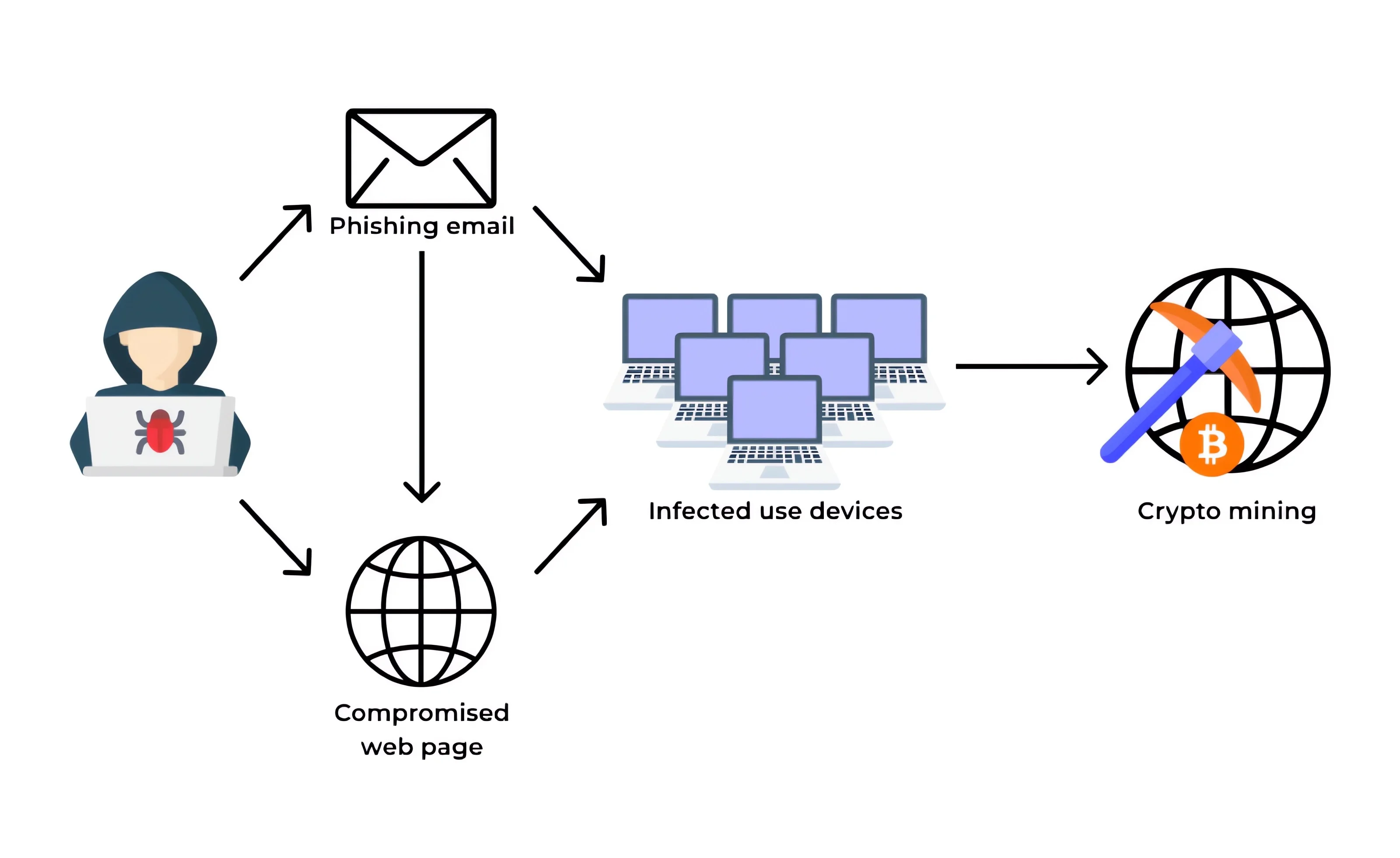
The process begins when a device gets infected, often through deceptive tactics like phishing emails, malicious ads, or compromised software downloads. Once installed, the malware runs in the background, often disguising itself as a legitimate process to avoid detection.
It then taps into the device’s CPU or GPU power to solve complex mathematical problems essential for cryptocurrency mining. As these problems are solved, new cryptocurrency coins are “minted” and sent to the attacker’s wallet, all without the device owner’s knowledge or consent.
It’s worth noting that a related threat, known as CryptoJacking, operates similarly but directly within web browsers without the need to install software on the victim’s device.
Common Symptoms of an Infected Device:
- Slowed Performance: One of the most noticeable signs is a significant slowdown in device performance. Applications might take longer to open, and tasks might become sluggish.
- Overheating: The increased computational work can cause devices, especially laptops and smartphones, to overheat, even when not running intensive tasks.
- High CPU or GPU Usage: A sudden spike in CPU or GPU usage, especially when the device is idle, can be a red flag.
- Increased Electricity Bills: As the malware uses more power, affected users might notice a rise in their electricity bills.
- Unfamiliar Processes: Checking the task manager or activity monitor might reveal unfamiliar processes consuming a large amount of resources.
Potential Risks and Damages:
- Hardware Wear and Tear: Continuous mining can lead to faster degradation of device components, reducing their lifespan.
- Loss of Productivity: A slowed device can hamper work, leading to lost time and potential income.
- Privacy Concerns: Malware often comes bundled with other malicious software, which can spy on users, steal personal data, or introduce ransomware.
- Financial Implications: Beyond increased electricity bills, there’s the risk of other malware types leading to direct financial losses, such as through stolen banking details.
Understanding the intricacies of crypto-mining malware is the first step in combating it. By recognizing the signs and understanding the risks, users can take proactive measures to protect their devices and data.
How to Detect Crypto-Mining Malware?
Crypto mining malware is particularly sneaky. It operates covertly, often leaving no overt signs of its presence. However, with a keen eye and the right tools, detecting this stealthy intruder becomes feasible. Here’s how you can spot the signs and confirm an infection:
Monitoring Device Performance:
- Unexpectedly High CPU Usage: One of the hallmark signs of crypto mining malware is a sudden and unexplained surge in CPU (Central Processing Unit) usage. Even when you’re not running any resource-intensive applications, you might notice your device’s fans working overtime or the system becoming noticeably slower. This is because the malware is using your device’s processing power to mine cryptocurrency. Regularly checking your device’s CPU usage through built-in system monitors can help spot any anomalies.
Using Specialized Tools:
- Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software: Modern antivirus and anti-malware programs are equipped to detect and remove a wide range of threats, including crypto-mining malware. Regular scans with updated software can help identify and eliminate these threats. Some software even offers real-time protection, alerting you the moment a threat is detected.
- Crypto Mining Detector Tools: There are specialized tools available designed explicitly for detecting crypto mining activities. These tools monitor network traffic and system processes to identify any crypto-mining patterns. Examples include ‘MinerBlock’ and ‘No Coin’, which are browser extensions that block crypto mining scripts on websites.
Checking for Unfamiliar Processes:
- Task Manager and Activity Monitor: Both Windows and macOS offer built-in tools (Task Manager for Windows and Activity Monitor for macOS) that display all active processes on your device. Regularly checking these tools can help you spot unfamiliar or suspicious processes that consume a significant amount of resources. If you notice a process that you don’t recognize or seems out of place, it’s worth investigating further.
4 Steps to Remove Crypto Mining Malware

Discovering that your device is infected with crypto-mining malware can be alarming. However, with a systematic approach, you can effectively remove this threat and restore your device’s health. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate this process:
Step 1: Boot your Device in Safe Mode
Why Safe Mode?
Safe Mode is a diagnostic mode in operating systems like Windows and macOS that starts your device with a minimal set of drivers and services. This restricted environment ensures that the malware doesn’t interfere with the removal process.
How to Boot in Safe Mode?
- Windows: Restart your computer and press the ‘F8’ key repeatedly before the Windows logo appears. From the Advanced Boot Options menu, select ‘Safe Mode’.
- macOS: Restart your Mac and hold down the ‘Shift’ key until the Apple logo appears.
Step 2: Scanning and Removal
Once in Safe Mode, run a full system scan using your trusted antivirus and anti-malware software. Ensure that your software is updated to the latest definitions to detect and remove the most recent threats. Follow the software’s prompts to quarantine or delete any detected threats.
Step 3: Manual Removal
1. Locating Suspicious Files:
Navigate to your device’s main hard drive and explore common malware locations like the ‘Temp’ folder in Windows. Look for unfamiliar files or files with random names, as these can often be malware payloads.
2. Deleting Suspicious Programs:
Check the list of installed programs on your device (Control Panel > Programs in Windows) and uninstall any unfamiliar or suspicious applications.
3. Registry Cleanup:
The Windows Registry is a database that stores low-level settings. Malware often creates entries here to ensure they’re run at startup.
- Caution: Editing the registry incorrectly can cause serious system issues. Always backup the registry before making changes.
- To access the registry, type ‘regedit’ in the Windows search bar and navigate to ‘HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE > SOFTWARE’. Look for unfamiliar entries and delete them. However, if unsure, consult with an expert or use specialized tools designed for registry cleanup.
Step 4: Browser Cleanup
- Removing Extensions and Add-ons: Open your web browser and navigate to the extensions or add-ons section. Remove any unfamiliar or suspicious extensions. Tools like ‘MinerBlock‘ can also be added to block crypto mining scripts.
- Resetting Browser Settings: Over time, malware can alter your browser settings, redirecting you to malicious sites or displaying unwanted ads. To counter this, reset your browser to its default settings. This can usually be found in the browser’s settings or options menu under ‘Advanced’ or ‘Reset’.
Post-Crypto Mining Malware Removal Steps
Successfully removing crypto mining malware from your device is a significant achievement, but the journey to ensure long-term digital safety doesn’t end there. Adopting proactive post-removal practices can shield your device from future threats and minimize potential damages.
Here’s a guide to fortifying your digital defenses:
1. Understanding the Crypto Mining Space
For those passionate about crypto mining, it’s easy to get lured by promises of quick profits. However, this can sometimes lead to unknowingly engaging with malicious entities. Remaining updated with the latest developments in the Bitcoin mining sector is vital.
Many online platforms, such as newsbtc, provide regular updates and insights into the mining industry. Leveraging the expertise from such sources can help enthusiasts, especially beginners, understand the changing dynamics, avoid pitfalls, and make informed decisions.
2. Regularly Updating and Scanning with Antivirus Software
Cyber threats constantly evolve, making regular software updates crucial. By keeping your antivirus software up-to-date, you equip it with the tools to combat new threats.
Set your software to run automatic scans and enable automatic updates, ensuring consistent protection without manual intervention.
3. Backing Up Important Data
While crypto mining malware focuses on exploiting device resources, other malware can jeopardize your data. Regular backups are a safety net, allowing swift recovery from potential losses.
Consider using external hard drives for periodic data transfers and reputable cloud storage services for continuous backups. Remember to use strong passwords and two-factor authentication for cloud services.
4. Staying Informed About the Latest Malware Threats
Awareness is a powerful defense. Familiarize yourself with the latest cyber threats by following cybersecurity blogs like KrebsOnSecurity. Engage in online forums such as BleepingComputer, where users share experiences and advice.
Additionally, attending cybersecurity webinars can provide deeper insights into current threats and protective measures.
5. Understanding the Regulatory Environment
The regulatory environment surrounding Bitcoin mining varies significantly across different regions. Some countries embrace this innovative technology, while others have imposed restrictions or outright bans.
When affected by crypto malware, it’s essential to understand your rights within this regulatory framework. Being informed about local regulations can guide your response and any potential recourse. If you’re in a region with stringent regulations against crypto-related cybercrimes, you might have more legal avenues to pursue action against perpetrators.
FAQs
Why is my legitimate crypto mining software flagged as malware by antivirus programs?
Antivirus programs are designed to detect and block potential threats to ensure user safety. Given the rise of malicious crypto mining activities (like cryptojacking and crypto mining malware), many antivirus solutions have become particularly sensitive to all types of mining software.
Even legitimate mining applications can exhibit behavior similar to malware, such as high CPU usage and accessing certain system processes. As a result, to prevent potential unauthorized mining, antivirus programs might flag and quarantine legitimate mining software as a precautionary measure. If you’re certain your mining software is trustworthy, you can whitelist it in your antivirus program to prevent future alerts.
What are some crypto mining software that are often flagged as malware by antivirus programs?
Several legitimate crypto mining software applications are frequently detected as potential threats by antivirus solutions due to their similarities in behavior with malicious mining scripts. Some of these include:
1. MinerGate: A popular mining software that supports various cryptocurrencies.
2. NiceHash: A platform that allows users to sell or buy hashing power.
3. CGMiner: An open-source GPU miner written in C and available for several platforms.
4. EasyMiner: A GUI-based miner that acts as a front end for CGMiner and CPUMiner.
5. BFGMiner: Similar to CGMiner but optimized for ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) mining hardware.
It’s essential to note that while these software applications are legitimate, they can be misused by malicious actors. If you’re using or planning to use any of these tools, ensure you download them from their official websites and whitelist them in your antivirus program to avoid unnecessary alerts.
How can I detect if my device is infected with crypto-mining malware?
Common signs include unexpected high CPU usage, device overheating, increased electricity bills, and unfamiliar processes running in the background.
Why is it essential to remove crypto-mining malware from my device?
Crypto mining malware can slow down device performance, increase electricity costs, cause hardware wear and tear, and potentially lead to other security and privacy risks.
How can I protect my device from future crypto-mining malware threats?
Regularly update and scan your device with antivirus software, back up important data, stay informed about the latest malware threats, and understand the crypto mining landscape and its regulations.
What is the significance of the regulatory environment in crypto mining?
The regulatory environment dictates the legal stance of countries on crypto mining. Some countries support the technology, while others have imposed restrictions or bans. Understanding these regulations can help users know their rights when affected by crypto malware.
Are there specialized tools to detect crypto-mining activities?
Yes, there are tools and browser extensions like ‘MinerBlock’ and ‘No Coin’ designed explicitly to detect and block crypto mining scripts on websites.
How does crypto-mining malware affect my electricity bill?
The malware uses a significant amount of your device’s power to mine cryptocurrencies, leading to increased power consumption and, consequently, higher electricity bills.
What should I do if my antivirus doesn’t detect the crypto-mining malware?
Consider booting your device in Safe Mode and using multiple antivirus and anti-malware tools for scanning. Manual removal by checking for suspicious files and processes can also be effective.
How can I stay updated on the latest developments in the Bitcoin mining sector?
Follow reputable online platforms and cybersecurity blogs, such as newsbtc, that provide regular updates and insights into the mining industry.
What are the potential risks of not addressing crypto-mining malware?
Unaddressed crypto mining malware can lead to hardware degradation, loss of productivity, increased electricity costs, and potential privacy breaches.
Related Posts:
- How to hack bitcoin wallet password
- 5 Essential Strategies for Protecting your Crypto from Hackers
- Bitcoin multiplier tool – Double your Bitcoins
- Tips to Protect Your Cryptocurrency from Hackers
