Fastening plays a crucial role in the world of electronics and electrical equipment. Whether it’s assembling circuit boards, mounting components, or securing electrical enclosures, the choice of screws is of utmost importance.
In this article, we will explore the technological advancements and the significance of self-tapping screws in electronics and electrical equipment, understanding their working principle, their applications, factors to consider, best practices, and overcoming challenges.
Understanding Self-tapping Screws
Self-tapping screws possess unique features that make them suitable for a variety of applications. These screws are designed with a sharp, self-forming thread that allows them to create their own mating threads when driven into a material.
This eliminates the need for pre-drilled holes, simplifying the assembly process. Self-tapping screws come in various types, including thread-forming and thread-cutting screws, each serving specific purposes.
Applications of Self-tapping Screws in Electronics and Electrical Equipment
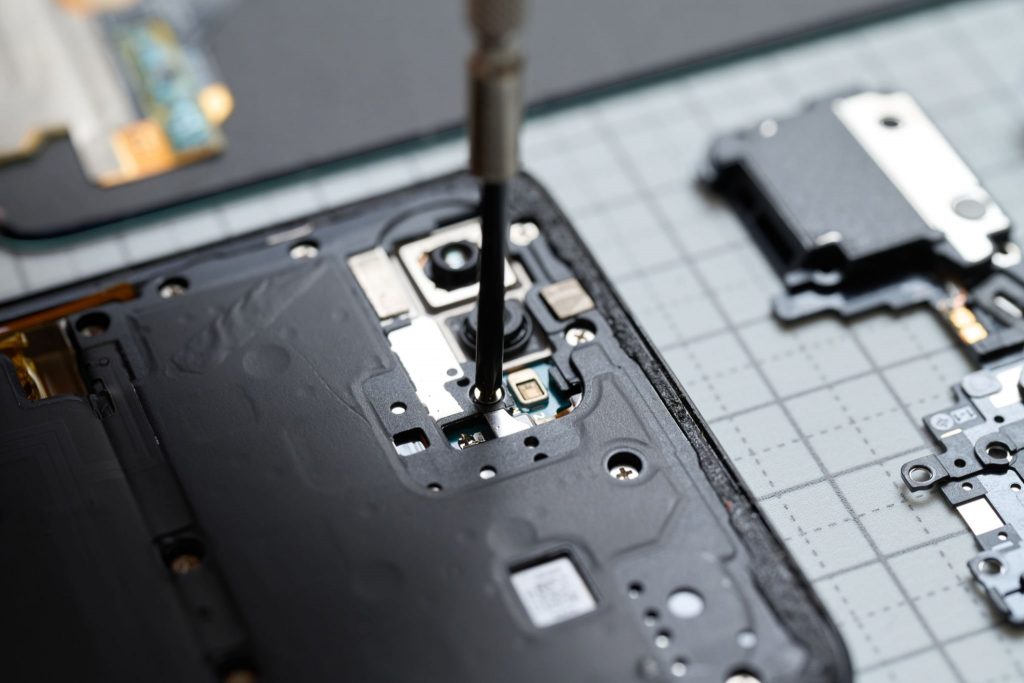
1. Fastening Circuit Boards and PCBs
Secure fastening is critical for reliable electrical connections in circuit boards. Choosing the right self-tapping screws ensures proper assembly and prevents damage to delicate components. Guidelines for installation, such as using the correct screw type and maintaining proper torque, are essential.
2. Mounting Components and Devices
Self-tapping screws are used to secure switches, connectors, terminals, displays, panels, and control interfaces. We explore the considerations for selecting appropriate screws, including size, thread type, and length, to ensure proper fastening of these components.
3. Assembly and Repair of Electrical Enclosures
Electrical enclosures require secure and durable fastening to protect the internal components. Self-tapping screws offer an effective solution for joining enclosure panels and covers. We delve into the importance of grounding and sealing considerations for these applications.
Factors to Consider when Using Self-tapping Screws in Electronics and Electrical Equipment
1. Material Compatibility and Electrical Conductivity
Different materials used in electronics and electrical equipment require specific screw choices to ensure compatibility and electrical conductivity. Understanding these considerations helps maintain optimal performance and safety.
2. Size, Thread Type, and Length Selection
Choosing the right screw size, thread type, and length is crucial for achieving proper engagement and avoiding damage. We discuss the importance of referring to industry standards and guidelines when selecting self-tapping screws.
3. Torque Requirements and Limitations
Applying the correct torque is essential for achieving secure fastening without causing damage. We highlight the significance of using torque specifications provided by manufacturers and employing torque-limiting tools to prevent over-tightening.
4. ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) Considerations
Electronics are susceptible to ESD, which can damage sensitive components. We explore how self-tapping screws can impact ESD and discuss precautions to mitigate the risks during installation.
5. Compliance with Industry Standards and Regulations
Compliance with industry standards and regulations is crucial for ensuring the reliability and safety of electronics and electrical equipment. We emphasize the need for using self-tapping screws that meet relevant standards and guidelines.
Best Practices for Using Self-tapping Screws in Electronics and Electrical Equipment
1. Preparing the Work Area and Components
Proper preparation of the work area and components ensures smooth and efficient installation. We discuss practices such as cleaning surfaces, organizing materials, and inspecting components before fastening.
2. Ensuring Proper Alignment and Hole Preparation
Achieving accurate alignment and preparing holes correctly are crucial for successful self-tapping screw installation. We provide guidelines for marking, aligning, and drilling holes to facilitate smooth engagement.
3. Using the Correct Tools and Techniques for Installation
Employing the right tools and techniques enhances the effectiveness of self-tapping screw installation. We discuss the importance of using screwdrivers or power tools specifically designed for self-tapping screws, as well as techniques such as applying steady pressure and maintaining perpendicular alignment during installation.
4. Applying the Appropriate Torque and Avoiding Over-tightening
Proper torque application is essential to ensure secure fastening without causing damage to the materials or components. We provide guidance on using torque wrenches or torque-limiting devices and avoiding the common pitfall of over-tightening.
5. Post-installation Inspections and Testing
Conducting post-installation inspections and testing helps verify the effectiveness of self-tapping screw fastening. We highlight the importance of checking for secure engagement, verifying electrical connections, and conducting functional tests to ensure optimal performance.
Challenges and Solutions
1. Common Challenges Encountered with Self-tapping Screws in Electronics and Electrical Equipment
We address common challenges such as stripping or damaging threads, loosening due to vibration, and limited space or access constraints that can complicate self-tapping screw installation.
2. Strategies to Overcome Stripping or Thread Damage
We provide tips and techniques to prevent or address stripping or thread damage, including using lubricants, employing thread-forming screws, and employing thread repair methods.
3. Addressing Vibration and Loosening Issues
Vibration can cause self-tapping screws to loosen over time. We discuss strategies to address this, such as using locking mechanisms, applying thread-locking compounds, or utilizing spring washers to enhance the stability of the fastened connections.
4. Dealing with Limited Space and Access Constraints
Installing self-tapping screws in confined spaces can be challenging. We suggest solutions such as using magnetic screwdrivers, flexible extensions, or alternative fastening methods like captive screws or panel clips when space is limited.
In the realm of electronics and electrical equipment, the choice and proper use of self-tapping screws are crucial for achieving secure and reliable connections.
By understanding the working principles, applications, factors to consider, and best practices, one can ensure optimal fastening results. Overcoming challenges through appropriate strategies and adherence to industry standards ensures the longevity, functionality, and safety of electronic and electrical systems.
By paying attention to the details and following the guidelines outlined in this article, professionals and enthusiasts can confidently utilize self-tapping screws to create robust and durable assemblies in the realm of electronics and electrical equipment.
