The Windows Task Manager, a tool many of us associate with the iconic Ctrl+Alt+Del command, has come a long way since its inception. Its journey began with Windows 3.0, where it was a simple utility to switch between applications or to terminate them.
Over the years, as Windows operating systems evolved, so did the Task Manager. With each iteration, Microsoft added layers of functionality, transforming it from a basic application switcher to a comprehensive system diagnostic tool.
No longer just a basic application switcher, by the time Windows 10 arrived, it had become an essential tool for both casual users and IT professionals. It’s not just about ending unresponsive programs anymore; it’s about understanding your computer’s performance, managing startup programs, and even diving deep into system processes.
The modern Windows 10 Task Manager offers a wealth of information and controls that many users might not even be aware of.
Note: As you explore this article, you might find it useful to have the Task Manager open alongside for a hands-on experience. If you’re using a dual-monitor setup and wish to move the Task Manager to your other screen, you can easily do so. For step-by-step instructions on how to move the task manager to another monitor, please refer to this guide on how to move task manager to other windows.
Beyond Ending Tasks
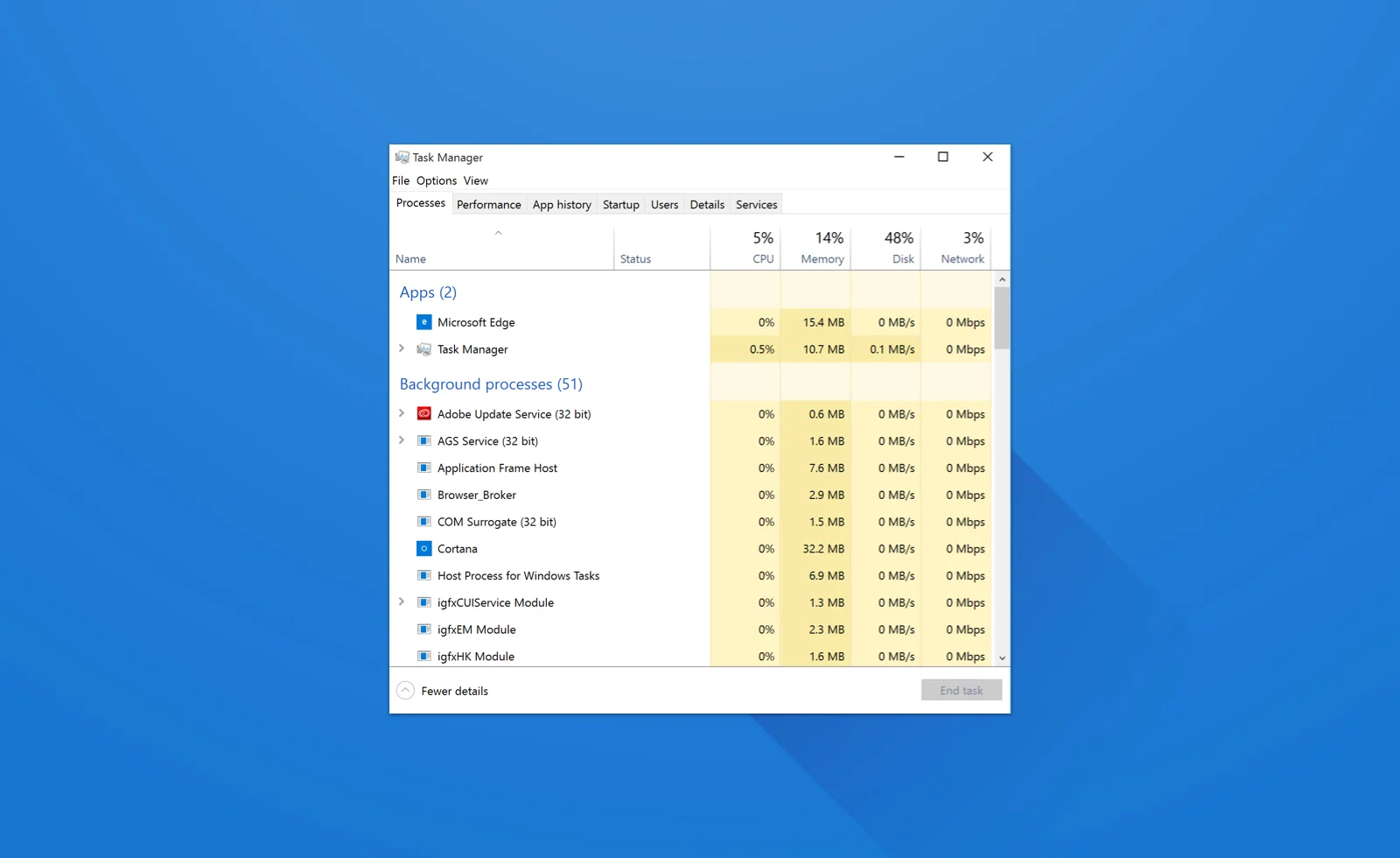
When most people open the Task Manager, they’re usually greeted by the “Processes” tab, which showcases running applications and their impact on system resources. But this is just the tip of the iceberg.
The Task Manager houses several other tabs, each offering a unique perspective on your computer’s operations.
- Processes Tab: This is where you can view all running applications and background processes. It provides insights into CPU, memory, disk, and network usage for each process, allowing users to pinpoint resource-hungry applications.
- Performance Tab: A real-time dashboard of your system’s health. It displays dynamic graphs for CPU, memory, disk, and network usage, giving a comprehensive view of how resources are being allocated and used.
- App History Tab: This section is particularly useful for tablets or PCs with a limited data plan. It tracks resource usage by Metro apps, helping users identify which apps are consuming the most data or resources.
- Startup Tab: Ever wondered why your computer takes a while to start? This tab lists all applications that launch at startup, allowing users to disable non-essential apps and speed up boot times.
- Users Tab: Get a snapshot of all users currently logged into the system and see the resources each user session is consuming.
- Details Tab: For those who want to dive deeper, this tab provides detailed information about each running process, including process ID, status, and memory footprint.
- Services Tab: A behind-the-scenes look at Windows services running on your system. Users can start, stop, or restart services directly from this tab.
Performance Monitoring in Windows 10 Task Manager
The Task Manager’s “Performance” tab serves as a real-time diagnostic tool, offering a visual representation of how your system’s resources are being utilized.
But how do we interpret these graphs and metrics?
- CPU Usage: This graph showcases the percentage of your computer’s processing power currently in use. A consistently high CPU usage might indicate an application or process that’s consuming more than its fair share of resources, potentially slowing down the system.
- Memory Usage: Memory, or RAM, is where your system stores data that’s actively being used. If this graph is consistently high, it could mean your system is running out of RAM, causing it to use the slower hard drive as a substitute, which can lead to decreased performance.
- Disk Usage: This metric indicates how actively your hard drive is being read from or written to. If this number is high, especially when you’re not actively using your computer, it could be a sign of background processes or updates taking place.
- Network Usage: Representing your computer’s network activity, this graph can help identify if applications are using more internet bandwidth than they should, which can be especially crucial for those with limited data plans.
Monitoring these metrics is more than just a tech enthusiast’s pastime; it’s essential for maintaining system health. By keeping an eye on these performance indicators, users can preemptively identify potential issues, optimize resource allocation, and ensure their computer runs smoothly.
Startup Impact and System Speed
Every time you boot up your computer, several applications spring to life in the background. While some of these are essential for system functionality, others might be slowing down your startup process more than you realize. The Task Manager offers a unique lens into this world, helping users optimize their boot times and enhance overall system speed.
Within the Task Manager’s “Startup” tab, you’ll find a list of all applications that launch when your system starts. More importantly, each application is labeled with its impact on the startup process: Low, Medium, or High. This “impact” metric is a game-changer, allowing users to quickly identify which applications are the primary culprits behind sluggish boot times.
By simply right-clicking and choosing to disable high-impact or non-essential applications, users can significantly reduce their system’s boot time. This not only means you can start working or playing faster, but it also reduces the strain on system resources, ensuring smoother performance once the system is up and running.
User Management and Advanced Details
The Windows 10 Task Manager serves as a central hub, not just for applications and processes but also for managing user sessions. Here’s how:
1. Managing User Sessions
Within the “Users” tab of the Task Manager, you can view all active user sessions on the computer. This is especially useful for shared computers or systems with multiple user accounts. From here, you can see which users are logged in, what applications they’re running, and how much of the system’s resources their processes are consuming.
If needed, you can also log off users or send them messages, ensuring optimal resource allocation and system performance.
2. Diving into Advanced Process Details
The “Details” tab offers a granular look at every process running on your system. Beyond just seeing the application’s name, you can view its process identifier (PID), status, and even the number of threads it’s using.
For those who want to go deeper, understanding system threads and handles can provide insights into how applications interact with the operating system and hardware.
3. UWP App History
Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps are a newer breed of applications designed to run across various Microsoft platforms seamlessly. The Task Manager provides a unique “App history” tab, allowing users to monitor the resource usage of these apps over time.
This can be invaluable for identifying resource-hungry apps and ensuring your system runs smoothly.
Hidden Features and Shortcuts of Windows 10 Task Manager
The Windows 10 Task Manager, while straightforward at first glance, is brimming with hidden features and shortcuts such as:
1. Always-On-Top Mode
Ever tried to diagnose a misbehaving application that’s covering your entire screen, making it hard to access the Task Manager? The always-on-top mode is your solution. By navigating to ‘Options’ and selecting ‘Always on top’, the Task Manager will always float above other windows, ensuring you can access it no matter how cluttered your screen becomes.
2. System Heat Maps
The Task Manager isn’t just about lists and numbers. The ‘Processes’ tab uses color-coded heat maps to visually represent resource usage. The darker the shade, the higher the resource consumption. This visual cue allows users to quickly identify resource-heavy applications at a glance.
3. Quick Access Shortcuts
Navigating the Task Manager can be even faster with a few handy shortcuts. For instance, pressing ‘Ctrl + Shift + Esc’ will instantly open the Task Manager. Within the tool, you can use the arrow keys for navigation and ‘Delete’ to end a process. These shortcuts can significantly speed up your workflow, especially when diagnosing issues.
Wrapping up, the Windows 10 Task Manager, often perceived as a simple utility tool, is genuinely a powerful instrument that offers a wealth of insights and functionalities. From monitoring real-time system performance to diving deep into advanced process details, it showcases Microsoft’s commitment to providing users with comprehensive tools to understand and optimize their devices.
Related Posts:
- Migrating OS From HDD to SSD Using Partition Manager Software
- How to Remove Crypto Mining Malware from Your Device
- How to Easily Introduce New Software or Technology to Your Team
- Why Partitioning Your Hard Drive Is a Smart Move for Your Data
