Airdrop scams and other crypto-related scams are on the rise like never before as an increasing number of people are dabbling in the crypto world.
From college students to founders and business owners, everybody is involved in crypto, and many are making fortunes out of it, especially newbie investors who are brave enough to take risks. In fact, according to a survey in the US, 30% of investors between the ages of 18 and 34 would easily prefer investing in cryptocurrency over company stocks or government bonds.
Of late, you might have noticed that crypto scams, especially airdrop scams, have become a hot topic of discussion. A lot of investors have lost millions of dollars in these scams. Some have even lost their life savings. A more detailed explanation of the airdrop scam can be found below.
Note: Recently, scammers have been using tactics like “social engineering” to trick people and steal their cryptocurrencies on Twitter. I have added this new scam to the list, which can be found in the 9th position.
1. Airdrop Scams
Airdrops, which refer to the free distribution of small amounts of a certain cryptocurrency to its community members, are often used as bait by scammers.
Scammers are getting really good at tricking the crypto community. They’ll set up fake social media accounts and websites that look just like the real ones for popular crypto projects. Then, they’ll announce fake airdrop events for real cryptocurrencies on these fake accounts.
Usually, their posts will have a link that takes you to a form on their fake site. Here, they’ll ask you to put in your Ether wallet address to receive free coins. But there’s a catch: They also want your private key. Many people don’t think twice and share their private keys.
The moment you give them your details, the scammer empties your wallet, leaving no evidence behind. Here is an example of a fake airdrop promotion for the EOS token:
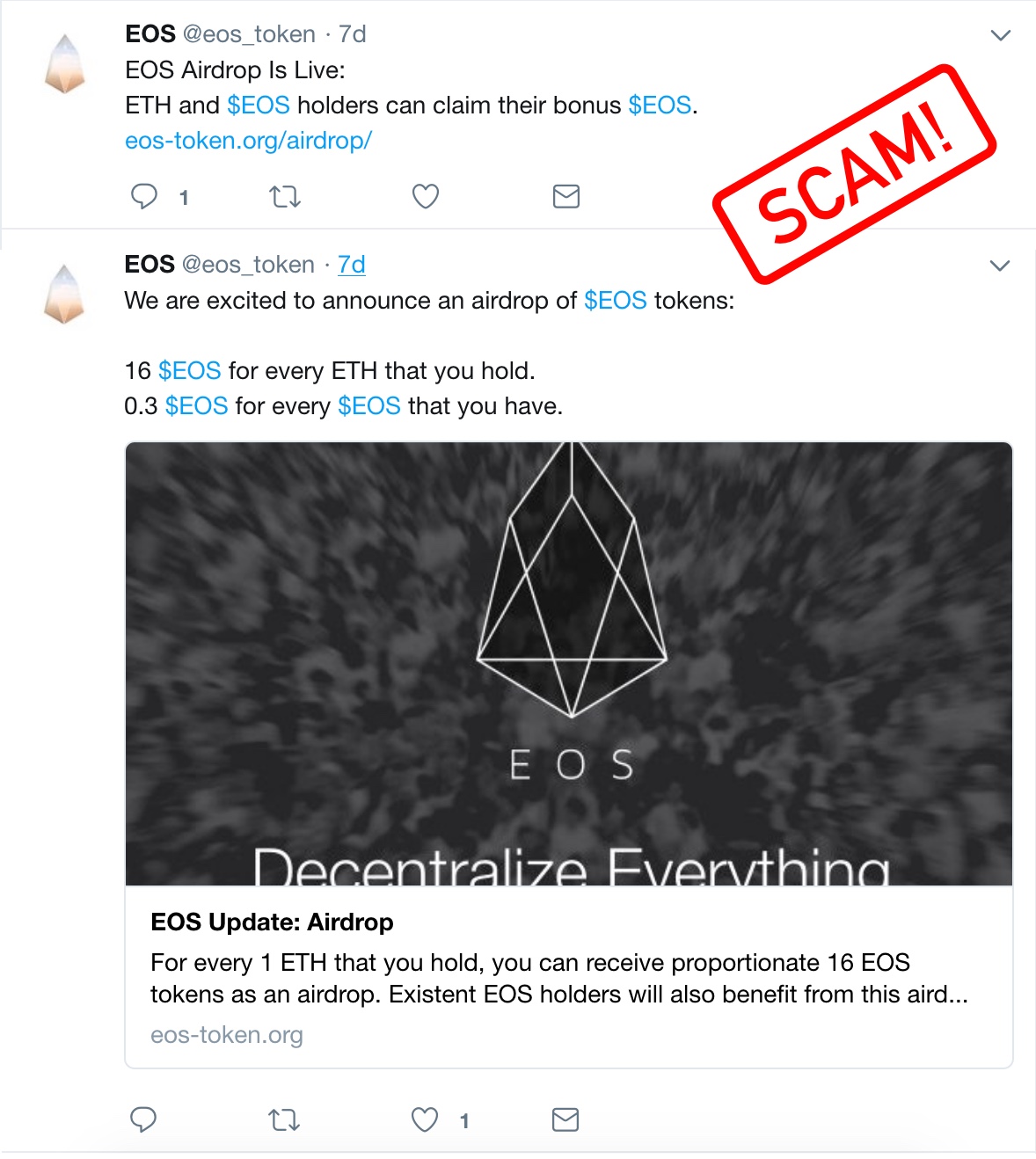
Staying vigilant against airdrop scams is crucial. To protect yourself, always do thorough research before participating in any airdrop. Avoid clicking on suspicious links, especially those sent via email or social media messages from unknown sources.
Genuine airdrops will rarely require you to send money or tokens in advance. Always double-check the official website of the cryptocurrency project and its social media channels to verify the legitimacy of the airdrop. Be wary of projects that ask for private keys or personal information, as these are red flags.
Lastly, make use of crypto communities and forums to gather feedback and insights from other users who might have experience with the same airdrop.
2. Pump and Dump Scams
The pump and dump scam is another shady scheme that is very popular amongst newbie traders. It is usually done by experienced traders with massive cryptocurrency capital, aka whales. It is often considered a way to make quick money.
Typical pump and dumb effect on cryptocurrency:
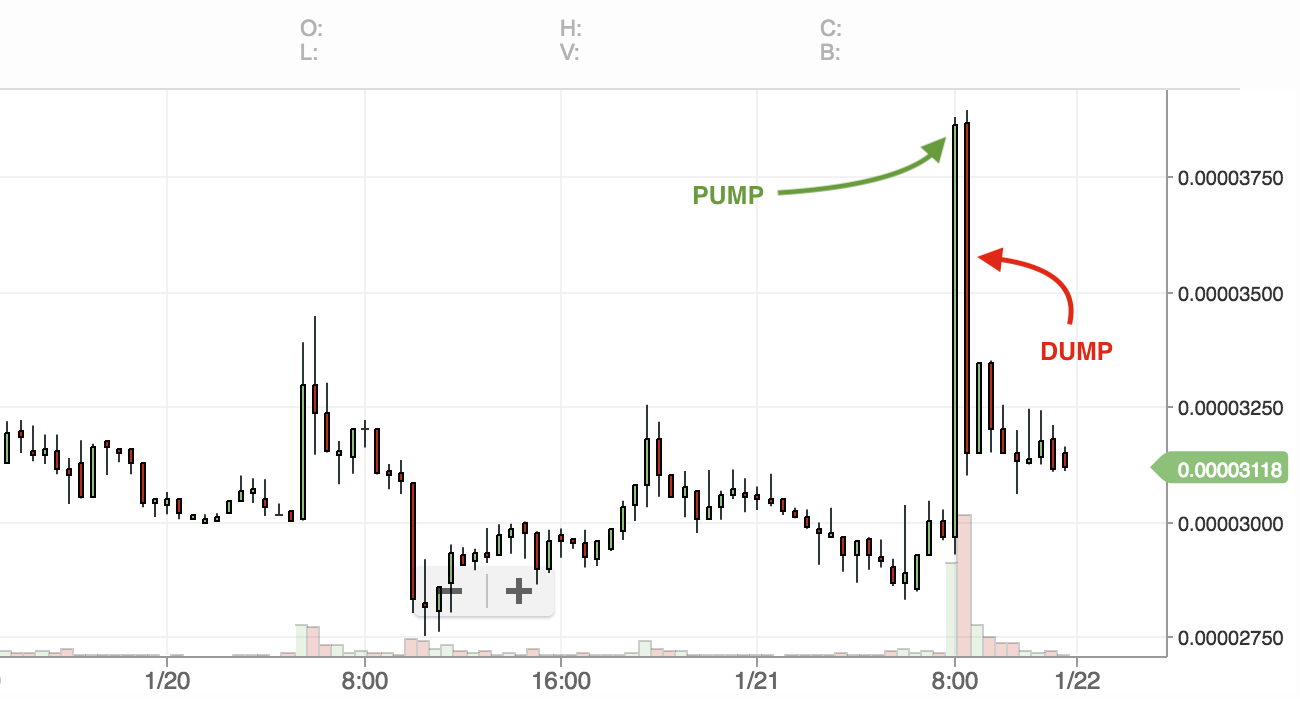
How does the “pump and dump” scheme work?
A trader or a group of cryptocurrency traders look out for a target coin with a low market cap and low trading volume. Once the coin is finalized, they start placing a huge amount of buy orders (PUMP) at the current price to make some crazy movements. This leads to a rise in the coin’s price.
As soon as the coin starts pumping, the traders inform their followers to invest in it. At this moment, the followers assume that the coin is soon going to pump and start buying it at a higher price, unaware of the already pumped-up price.
Here comes the catch: the traders who had initiated the pump had already placed the sell orders at a pumped-up price, which would eventually be sold out to their followers (DUMP). Thus, the followers end up losing their money as soon as the coin price drastically drops.
What’s more, scammers have created “pump & dump” groups on various social networks. Telegram being very popular, there are dozens of “pump & dump” channels that give out trading signals to their followers.
The only ones that really win out are the ones who operate “pump and dump” groups, because they and their friends buy in before the pump and leave many people within the group hanging.
Do yourself a favor and never participate in any kind of “pump and dump” group.
3. Malicious Cryptocurrency Trading Apps & Bots
Trading apps basically do two things: they provide the facility of holding your cryptocurrency tokens, and they give you the ability to buy and sell cryptocurrency tokens whenever you want. Most cryptocurrency exchanges facilitate trading, and few of them have an app for easy access.
Since many exchanges provide REST APIs to allow you to programmatically perform nearly all actions you can from the web interface, a number of third-party trading apps are floating in the market.
Many of them provide automated trading options, wherein a trading bot will trade on behalf of you so that you maximize the profits. However, not all of them are trustworthy.
A typical malicious trading app will ask you to first deposit or transfer cryptocurrency to your account Or it will ask you to input your existing wallet address & private key. Once you do this, the app suddenly stops working or will suspend your account without warning.
The scammers on the other side with your public and private key would soon empty your wallet without your consent.
So always be skeptical when it comes to trading apps, Don’t fall for the excellent reviews on 3rd party websites. Always check reviews and ratings in the Appstore.
I’m not here to spread fear without offering you some good news: there are some excellent trading apps out there. One such trading app which I personally use is BINANCE APP. I hold a number of altcoins there, and I’ve never had any trouble with them.
4. Fake Cryptocurrency Wallets
A “cryptocurrency wallet” is a collection of a keypair that consists of a “public key” and a “private key”. The “address” you send people is the public half and the private half resides in your wallet file. Now if a person has X cryptocurrency, he has to have a wallet to hold them.
This wallet can be in the form of hardware (hardware wallet) or in an online digital form (Digital wallet). And just like fake trading apps, there are fake digital wallets as well.
These fake wallets contain a keylogger program that steals your sensitive information and makes unwanted transactions. The problem is that these fake wallets easily appear in mobile app stores and hardly get audited until the investors lose their money.
5. Fake Coin Promotion (Ponzi Scheme)
Many cryptocurrencies have seen significant growth. While some truly earned their value, others were simply overhyped. Scammers use these success stories to promote their own fake coins, playing on people’s excitement. Those less informed often become victims of such scams.
We think we’re clever enough to spot a scam when it is in front of us. But if someone who is really confident of his product pitches you to invest in his business in a room full of investors, It’s pretty much hard to avoid being lured into it.
This is what happened when a young man in India was allegedly delivering a sales pitch for a cryptocurrency that did not exist. When arrested, he had already duped hundreds of people by luring them into investing.
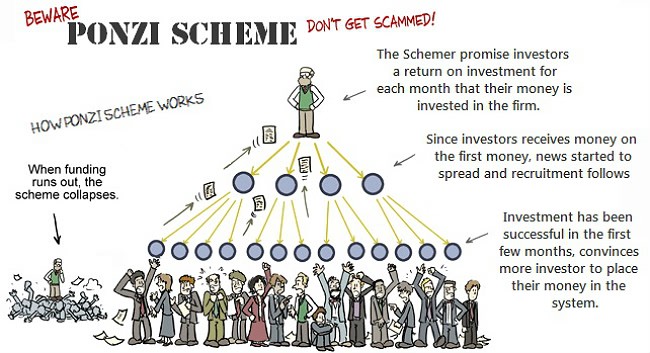
Scammers like these often organize lavish seminars to lure bigshot investors who then pitch in their referral connection to smaller investors. The scam involves a typical pyramid scheme, wherein you get paid more when you bring in more investors down the line. This kind of scam is often offline-based, and you are more likely to figure it out if you have had indulged in Pyramid & Ponzi schemes before.
6. Initial Coin Offering Scams (ICO scams)
ICO (Initial coin offering) is a way of raising substantial funds from investors for a blockchain project. Investors are given tokens/cryptocurrency in exchange for fiat currency. Any individual who wants to invest in a blockchain project can purchase the tokens from its developers during ICO sales.
ICO’s have become very popular and every new ICO sale attracts thousands of investors who are inspired by previous ICO performances, like that of NEO COIN which went from the ICO price of 3 cents to over $150 within 36 months.
Seeing this opportunity, Scammers are coming up with their own Blockchain projects which essentially do nothing, except having a fancy problem-solving approach in their whitepapers which can be easily bought for as little as a few hundred dollars. With little marketing, they end up getting attention from crypto enthusiasts who then give them a shout-out on social media & crypto channels.
This causes irrational exuberance among a wide range of crypto community, which then leads to considerable participation of investors in their futile ICO sale. And as soon as their token becomes vastly overestimated, The scammers start dumping their crypto tokens which eventually leads to an enormous price drop. The investors are left with no choice but to sell their crypto tokens with huge losses.
Again, I don’t want to spread FUD, there are some excellent ICO’s which look promising in solving real-world problems. Before investing do your own research, Check industry sites like CoinDesk, IcoWatchList, IcoAlert to verify the legitimacy of a claimed ICO.
Don’t fall for “too good to be true” offers, especially when received over email, advertisements or social media messaging.
The most prominent ICO scam was Enigma ICO Scam. In this scam, hackers took over Enigma’s official site and social media, changed the payment details, and tricked investors into sending them money.
Also, take a look at this wonderful post by BlockGeeks to avoid getting duped by ICO scams.
7. Phishing & Phone Porting Attacks on Wallet Holders
Phishing is far deadlier than all of the above scams. It’s the old-school way to get sensitive information from crypto investors. A single phishing attack on any of your accounts is enough for a hacker to figure out other sensitive information related to you.
Here is how scammers target their victims:
- They hunt and shortlist crypto investors from various social channels who are easily swayed to give out their details.
- They then identify their holdings with various cryptocurrency exchanges and wallets services.
- Using social engineering tactics, they obtain their email address which is linked to their wallet/ trading accounts.
- Finally, they start spamming their target user with phisher email crafted to sniff away the login credentials.
- If the victim falls for it, The scammer drains their wallet.
A phishing email targeting “Bittrex Exchange” users:
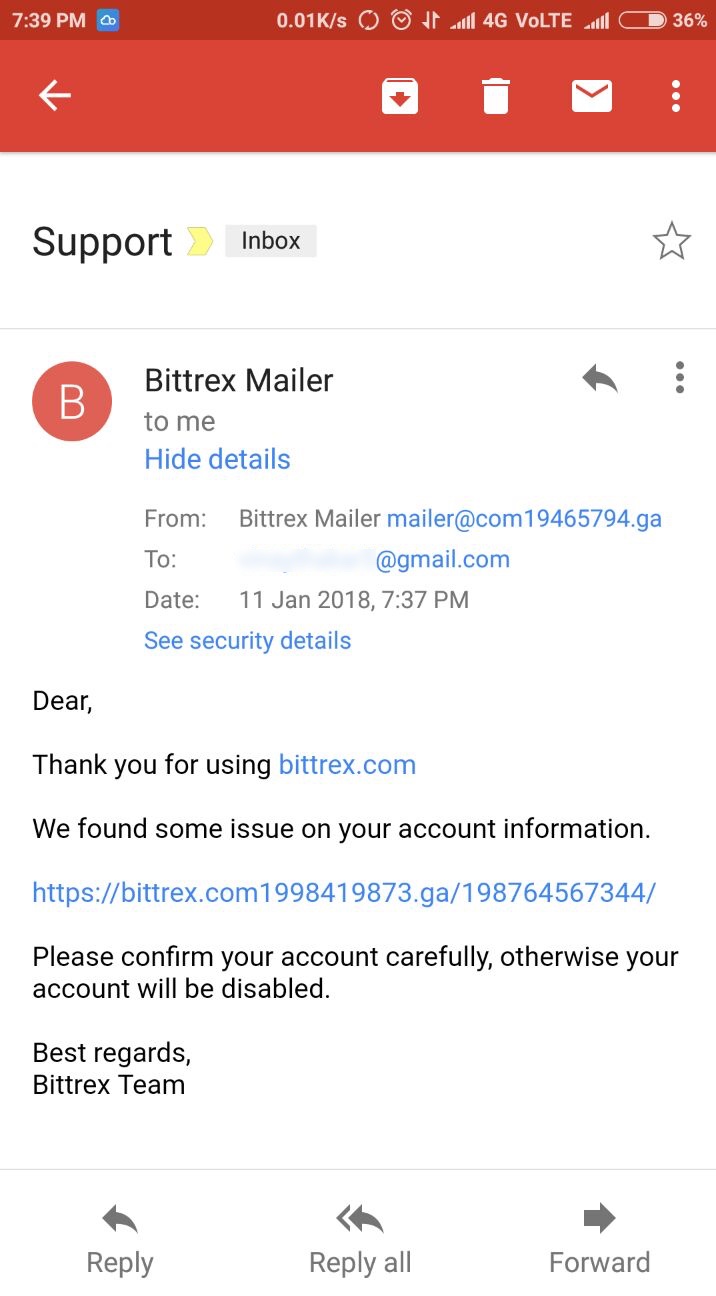
It’s easier to identify the phishing email while on a desktop since most email clients will show you the senders full email and you can always hover over the links to see the destination URL.
However, if you happen to be on your cellphone, the email client might not show you the senders email address unless you click “view details”. So always remember to verify the sender details before clicking any links in the email.
Since most crypto wallet services and exchanges have adopted 2-factor authentication which can also be used to reset passwords, scammers are also indulging in Phone-porting attacks.
Phone-porting is when scammer takes possession of a person’s phone number by tricking the mobile provider into giving them control of the account. Once he gets control over victim’s cellphone, he can easily opt to reset the password using SMS verification.
As discussed in the phishing section, the modus operandi remains the same. Instead of email, they acquire the cellphone numbers of their victims who then fall prey to Cell phone identity theft.
A solution for this is to switch two-factor authentication from SMS to Google Authenticator service.
8. Bitcoin Cloud Mining Scam
Ever since bitcoin got popular, a lot of cloud mining companies started surfing online who rent out their mining hardware for a fixed price to their customers. The customer who buys mining service gets paid mining profits monthly or yearly, which is often a small fraction of the money he invested.
You would say, If you had mining hardware running, and it would earn you money, why would you rent it out to strangers on the internet? The only logical answer to that is because by renting out hardware mining companies do not have to depend on mining profitability. Even if mining is not profitable, they get a steady income.
Since mining companies do not have to worry about paying their customers immediately, It can be a lucrative scam business opportunity. Check out uncle scam’s video explaining how you can set up a fake cloud mining business.
9. Imposter Scams [New]
An imposter scam is a scam wherein the scammer uses fake celebrity social media accounts, preferably Twitter to dupe people into sending small cryptocurrency donations in return for a chance of being sent 10 times worth of cryptocurrency back.
Here’s a fake Twitter account of ‘Tim Cook’ replying (pitching his scam) to the real Tim cook’s tweet, creating an impression that the tweet is from the real ‘Tim Cook’ per se.
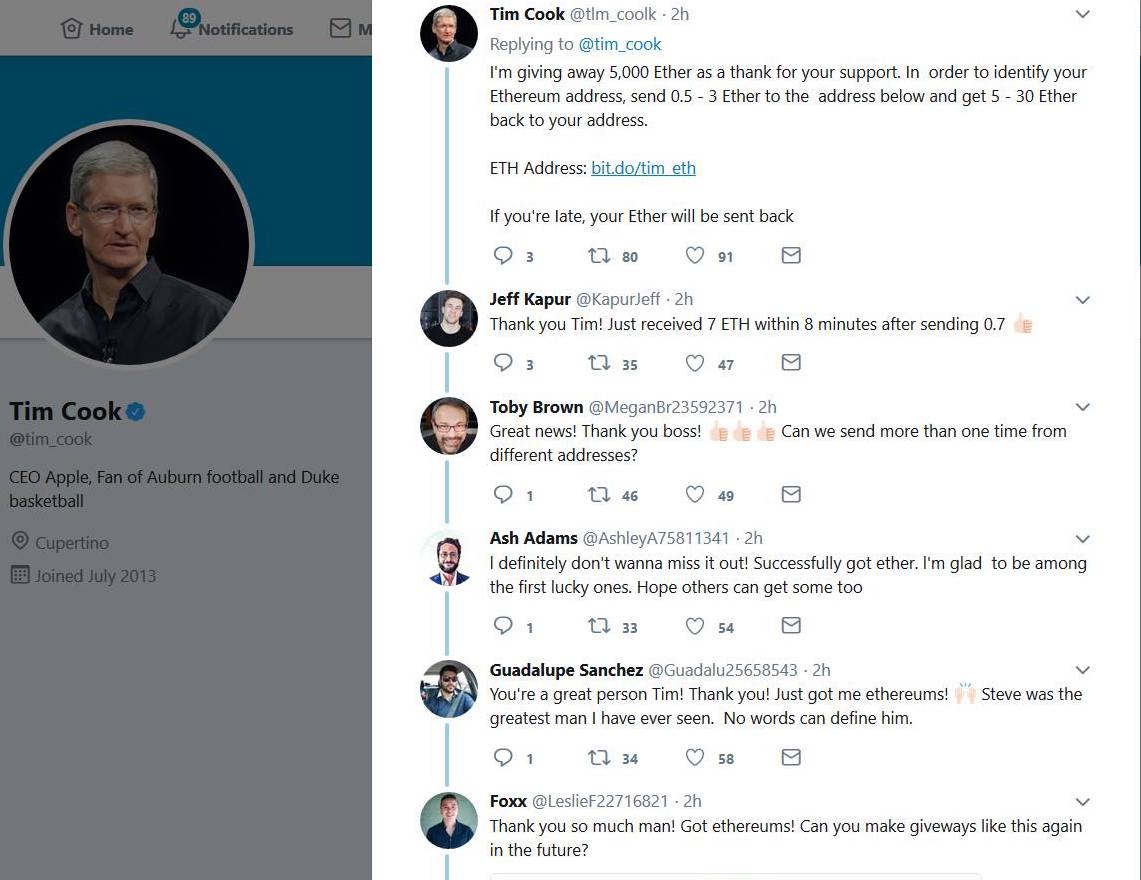
You can see the tweet from fake ‘Tim cook’ has garnered a lot of likes and replies that look genuine. No, wait! all those replies are made by the same crooks. The modus operandi of crooks carrying out imposter scams is, They first create a fake account of a popular tech celebrity along with another 5 to 6 fake Twitter accounts that impersonate normal Twitter users.
Once they have their weapons ready, the scammer starts tweeting his “scam text” to real celebs latest tweet as a reply. Quickly garners fake likes and retweets on his reply, which makes it a top reply to that tweet. He then uses his other fake accounts to respond to his tweet claiming to have received the promised funds.
How to spot Imposter scams on twitter?
Many of the imposter accounts are quickly being suspended by Twitter, however, a new account can be set up in under a minute. Spotting fake accounts of celebrities is quite easy. Always look for a ‘verified’ tick, Most real profiles will have a ‘verified’ tick.
Other warning signs include a low follower count and a Twitter handle that contains unnecessary letters or numbers to make it look like a real Twitter handle. This kind of imposter scam is evident on Facebook as well.
In crypto scams, once you lose your money, there’s usually no way to get it back. Considering the scams we’ve discussed, investing in new blockchain projects without proper knowledge is risky. To stay safe in the crypto world, thorough research is essential. If you truly believe in a project, then it might be worth the risk.
Citations
- Zohar, A. (2015). Bitcoin: under the hood. Communications of the ACM, 58(9), 104–113.
- Bonneau, J., Miller, A., Clark, J., Narayanan, A., Kroll, J. A., & Felten, E. W. (2015). SoK: Research perspectives and challenges for Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies. In 2015 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy.
- Vasek, M., & Moore, T. (2015). There’s no free lunch, even using Bitcoin: Tracking the popularity and profits of virtual currency scams. In International Conference on Financial Cryptography and Data Security (pp. 44–61). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Related posts:
- Never ask someone to create a BITCOIN wallet for you
- Immediate Edge Australia Scam – Crypto Trading Scam
- How to hack bitcoin wallet
- Bitcoin hack tool to generate bitcoins
- How to protect your crypto from hackers
- Bitcoin doubler- multiply your bitcoins
- Is it Safe to Keep your Bitcoins in Crypto Exchanges?
- 5 Reasons Why You Should Create a Bitcoin Wallet on iOS
